Question.
What does masking effect mean?
Answer.
There is countless variety of sound that exists on earth we live in. Fortunately, we are not able to hear all of these sounds.
Amongst these sounds, unpleasant type of sound present in the zone of audibility (frequency 30Hz-20Hz) is referred to noise.

As you could see in the chart above, noise can threaten our physical and mental health depending on the strength of the noise.
The level of road noise experienced during driving can hurt our health.
Chart below created by a prestigious car magazine shows the road noise heard inside the car during the driving speed of 130Km.

< Reference: German Autobilt Magazine >
-Test Condition: Decibel tester / 2 times running average / window closed, air conditioner, radio turned off / driving is automatic D mode-
Car has become such a necessity to modern day lives that contemporary man and woman cannot even imagine their days without cars.
As the saying “if you cannot avoid it, enjoy it” implies, we wanted to find a solution that could resolve this road noise problem.
Advanced sound technology has been a great help in finding the answer.
We could commonly hear songs playing in the elevator. Why do they play these songs?
This is to prevent any psychological anxiety that could come to the person on board by covering the wind separating sound of high-speed elevator.
Such phenomenon where one sound covers the other sound is called a “masking effect”.
This principle is easily utilized in many different places in our lives; for example, malls, restaurants, and hotels play the BGM to offset the noise in the space.

With this, one could ask if playing the song in louder volume in purpose of masking will increase the noise level.
When background music is played at 60dB over the noise of 50dB for masking effect,
the actual sound heard in our ear is offset by about 45dB, leaving the music to be heard and the noise to be smaller.
< Range of Masking Effect >

Most of the driving noise of a car occurs in mid-low frequency and this noise is louder in diesel cars than gasoline cars.
This noise can be offset by masking effect.
< Change of audible frequency >
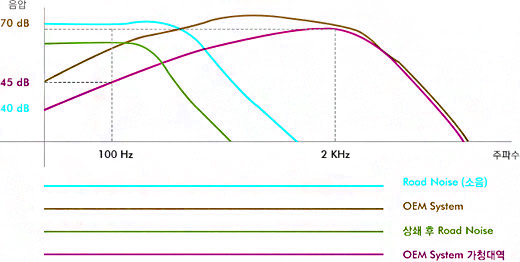
In case of road noises, if the volume of the OEM audio is increased to maximum frequency of road noise created by midsized vehicle driving at speed of 100Km (70dB sound pressure),
slight reduction of the road noise can occur due to masking effect, but also leaves lower frequency noises unmasked.
With frequency heard through OEM audio, lower frequency noise will be offset but high frequency noise gets left behind;
this causes the frequency range concentrating effect, causing the mid-high frequency noise to become a louder and more aggressive noise.
Actual road noise masking cannot be effectively applied,
because OEM audio system lacks the capability to produce low frequency band where substantial noise is concentrated.
For efficient application of masking effect for road noise, OEM audio needs to be capable of fulfilling the lacking mid-low frequency range.
This is one other reason for you to upgrade to TICKEN SOUND LAB’s SOLUTION.